Wearable devices that are worn on the body and used have become familiar devices due to the spread of smart watches.
For health management of individuals and corporations in the medical industry, and for reducing the work burden of employees in the long-term care industry.
The movement to utilize wearable devices has spread.

The development of wearable devices began in the 1990s, and although they were put into practical use around 2000, they did not spread widely. After that, it was 2013 that was called the "first year of wearable devices" in the industry. This is because it has become possible to link with the explosively popular smartphones and cloud computing, and as devices have become smaller, consume less power, and have lower costs, devices suitable for various purposes have appeared one after another. ..
Currently, there are a wide range of movements to utilize wearable devices, such as health, sports, crime prevention, transportation / transportation, tourism, communication, and entertainment, but in the "health field", efforts began early on, and various devices and mechanisms were developed. It has been. According to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications' IoT International Competitiveness Index (2018 results), the market share of wearable devices in the health field is the largest in the United States at 62.8%, followed by China at 17.3%, Finland at 13.4%, and Japan / Netherlands. Each is followed by 3.0%. It should be noted that the sales growth rate of Japanese companies exceeds 200%, which greatly exceeds the global market growth rate of about 10%, and the need for wearable devices in the health field in Japan has increased, and each company has increased its needs. It can be said that the development of is progressing.
Among the biometric information useful for health management, the main information that can be obtained from the wearable device includes the number of steps, distance traveled, calories burned, heart rate, body temperature, sleep time, and sleep quality. The feature of these data is that by visualizing, you can easily grasp your own internal rhythm and life rhythm. Furthermore, the development of a system for centrally managing these multiple data on smartphones and personal computers has made it possible to manage health more practically. There is also a health service that identifies "information requiring attention" from the biological data that is updated daily and issues an alert to the person.
On the other hand, health management using wearable devices is beginning to be actively used not only by individuals but also by businesses. Some companies provide employees with terminals and collect various biometric data so that they can check them from the in-house portal site and encourage self-care. Based on the accumulated data, industrial physicians and public health nurses provide health support to help prevent obesity and lifestyle-related diseases.
What is expected in this field from now on is utilization for mental health. A mechanism is being considered in which a decrease in concentration and a degree of stress accumulation are detected from the data of the terminal, and an alert is issued to the person when the danger zone is exceeded to encourage a rest. This year, many people feel anxiety and stress due to the change in their lifestyle due to the influence of COVID-19. Research is also being conducted to find signs of mental disorders from sleep, heartbeat, arm movements, etc., and support using wearable devices will be provided in the future.
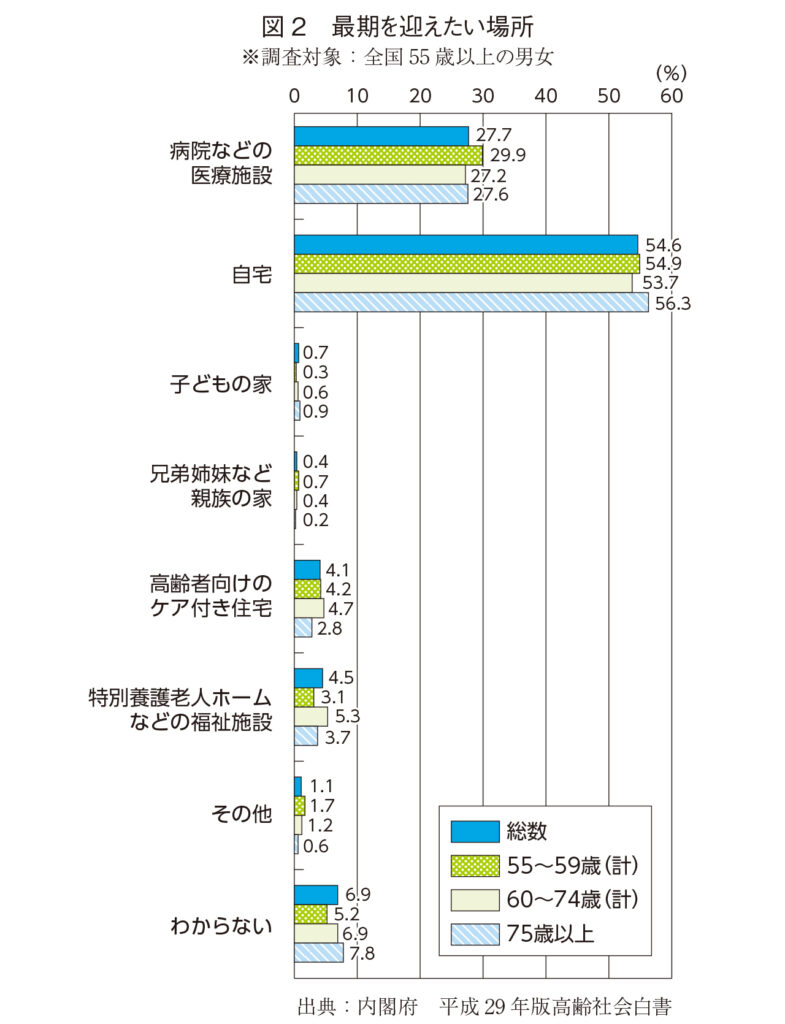
According to the Cabinet Office's "White Paper on Aging Society 2017", in Japan, "places where you want to receive long-term care" and "places where you want to reach the end" are most often "home", and many elderly people want medical care at home. (Figs. 1 and 2) Therefore, in the medical and long-term care industry, the need for remote control is increasing, and there are a number of cases of effective disease management, long-term care, or prevention using wearable devices that can be constantly monitored.
The world's first excretion prediction device is a mechanism that detects and analyzes changes in the bladder with an ultrasonic sensor attached to the lower abdomen of the elderly receiving care, and notifies the care worker's smartphone of the timing of excretion. By predicting excretion, appropriate toilet guidance can be performed, which reduces the burden of excretion assistance for care workers by about 30%, prevents unexpected incontinence, reduces the amount of diapers and pads used, and reduces the amount of diapers and pads used. In some cases, it is not necessary to wear diapers. This device has been certified as a target tool in the IT introduction support project "IT introduction subsidy 2020" for improving productivity of services promoted by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry this year, and can receive subsidies for device introduction costs.
Recently, devices that can visualize the activity state of one's own brain have also appeared. By measuring changes in cerebral blood flow using weak near-infrared light, this device can confirm the presence or absence of activation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which controls intellectual activities such as thinking and memory. A service that constantly provides personalized cognitive function training by using a smartphone app to perform cognitive function training and linking it with this device during that period was also provided this year.
In this way, wearable devices are also useful for improving the quality of life (QOL) of individuals in the field of extending healthy life expectancy such as disease prevention and long-term care prevention. It will be used more widely in the future, and will become an indispensable item to support our health and long-term care in the near future.
Figure 1: Places where you want to receive long-term care * Survey target: Men and women aged 55 and over nationwide
Source: Cabinet Office 2017 White Paper on Aging Society
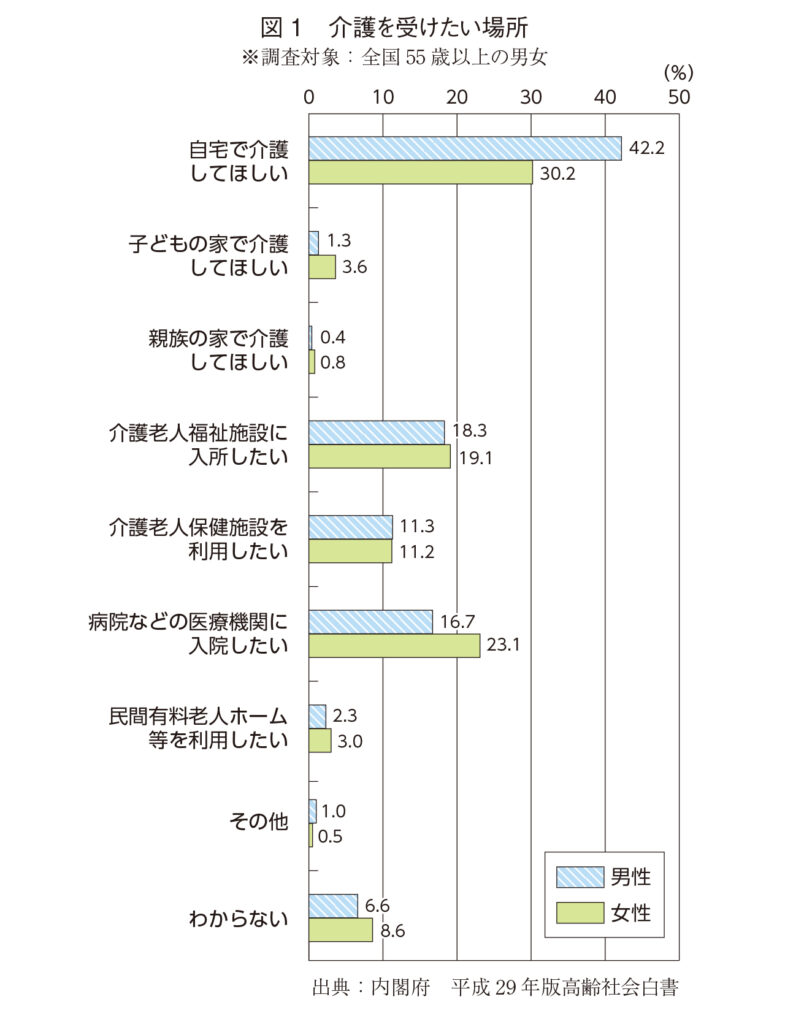
Figure 2: Places where you want to reach the end * Survey target: Men and women aged 55 and over nationwide
Source: Cabinet Office 2017 White Paper on Aging Society