ASOURCE®TIMES
今年3月から商用サービスが開始された第5世代移動通信システム(5G)。
あらゆるモノや人をつなぎ、IoT時代の重要な基盤として期待されている。
医療界においても遠隔診療を中心に5Gを活用したさまざまな実証実験が行われている。
※2020年6月の状況を反映

約50年前に始まった日本の遠隔診療は、法整備・解釈の問題や通信速度の制限により、近年まで読影を中心とした画像診断サービスに留まっていたが、通信技術の進展や、スマートフォンなどの情報通信機器の普及によって、遠隔診療の通信における技術的課題はほぼ解消された。法整備・解釈の問題においては、厚生労働省が2015年に遠隔診療の対象を明確に例示し、2018年には「かかりつけ医機能」を強化・推進するため、再診のみオンラインや電話での診療(オンライン診療)による保険診療を認めるなど、一定のルール整備が行われ、遠隔診療の適切な実施と普及へ向け動き始めている。
さらに今年4月、厚生労働省は新型コロナウイルス感染症の拡大防止策として、時限的・特例的な措置ではあるものの、初診でのオンライン診療も認めることとした。こうした遠隔診療における条件の緩和や技術的課題の解決により、医療機関・一般の人々の関心も急速に高まっている。
また、この3月から商用サービスが始まった5Gの登場によって遠隔診療はさらに発展することが期待されており、数年前から5Gを活用したさまざまな実証実験が全国各地の医療機関で行われている。
5Gでは、2時間の映画を3秒でダウンロードできるほどの超高速化・大容量化が実現される。これまでも僻地の診療所と都市部の大学病院をネットワーク回線でつないで共同診療することは行われてきたが、5Gによって、診療所から4K高精細カメラで撮影した患部の画像を大学病院に高速伝送することが可能になる。
実証実験に参加した医師によると、その画質は驚くほど鮮明で、診断の質が高まったという。また、会話も遅延することがないため、目の前で話しているような臨場感があり、遠隔で診療することにストレスを感じないそうだ。5G時代の到来で遠隔診療が重要かつ有効な診療形態のひとつとなり、地域の医療格差の解消にも貢献すると期待される。
現状のオンライン診療でも、医師不在の飛島や中山間地のある山形県では、県が環境整備を進めたこともあり、全国トップである30%以上のオンライン診療普及率を誇っている。(厚生労働省オンライン診療対応医療機関リストより)しかし、高齢者の多い地域など依然として普及率が低い自治体もある。これには高齢者対応の難しさ以外にも、対面診療に比べての診療報酬の低さ、システムの導入コスト、セキュリティ面への不安など様々な理由がある。
今後は各医療機関が抱える遠隔診療の問題点に対し、行政が積極的に支援や環境整備を行うことが遠隔診療普及の鍵となるだろう。
その他の遠隔診療のユニークな試みとしては、遠隔でのデジタル聴診器の利用があげられる。まず患者は聴診するポイントを番号で示した検査着を着用する。そして遠隔地にいる医師から画面越しに指示された検査着の番号に患者自身が聴診器を当てる。すると、患者の心音や肺音がリアルタイムで遠隔地にいる医師に伝送され、診断材料の一つになるという仕組みだ。すでに在宅医療の現場ではデジタル聴診器と遠隔診療を組み合わせ、高齢者に多い呼吸器疾患の早期発見につなげる試みが始まっており、今後5Gを利用したより高音質での伝送も計画されている。
5Gには高速通信だけでなく100個程度の機器やセンサーを同時にネットに接続できる「多数同時接続」、通信ネットワークにおけるタイムラグを極めて小さく抑えられる「超低遅延」といった特徴がある。こうした5Gの特徴を最大限に生かした遠隔手術支援の実証実験が、脳外科分野で進められている。
脳外科分野では近年、手術の精度と安全性の向上を図る「スマート治療室」の開発が行われてきた。これは、手術室にある複数の医療機器をネットワークで接続する、その場で撮影したMRI画像をはじめ患者の生体情報、手術の進行状況など、さまざまなデータを統合して1つのモニターに表示する、それを遠隔地にいる熟練医が確認しながら手術室にいる執刀医にアドバイスする、という仕組み。これまでの通信技術ではモニター室と手術室は同一施設内でしか接続できなかったが、5Gを活用することで遠隔でも手術支援を行うことが可能になってきた。
このように、今後は診断だけでなく治療の分野でも遠隔診療が着実に広がっていくだろう。しかし、日本医師会は「情報がない中での問診や視診だけでの診断・処方は危険」と述べており、初診からのオンライン診療については極めて慎重である。オンライン診療を含めた遠隔診療においては、対面診療と対比し優劣を決めるのではなく、入院・外来・在宅と並ぶ新たな診療形態として、発展する技術とどのように組み合わせ適用していくか、さらなる事例の収集や活発な議論が必要だ。
図 5Gの医療応用への期待
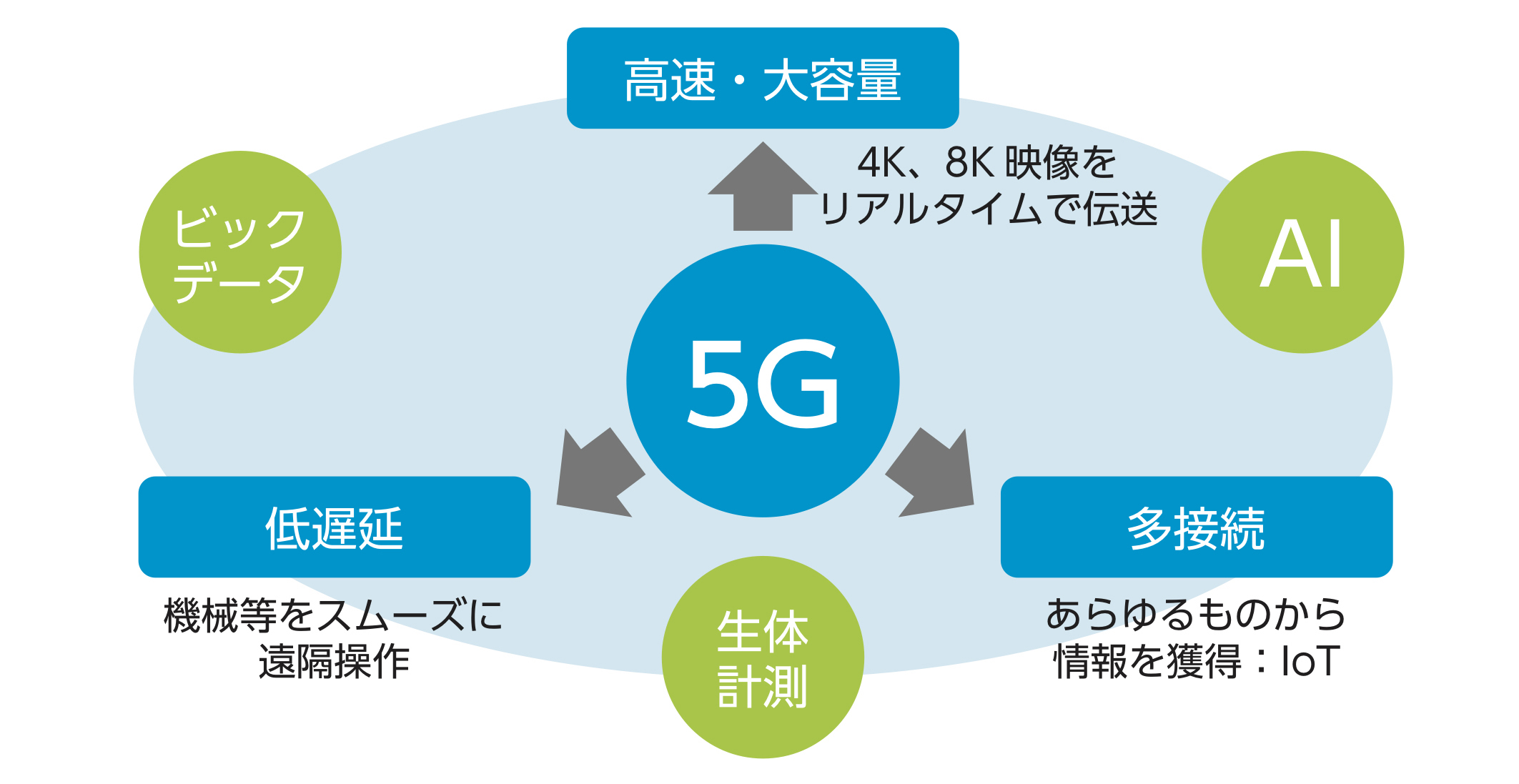
出典:日本医療機器テクノロジー協会 5G 時代に向けた日本の医療機器産業 界の取り組み
https://www.mtjapan.or.jp/jp/mtj/cn/pdf/hospeq2019/jp_01.pdf