
Director, Medical Safety Department, Toranomon Hospital
Junko Echigo
Graduated from Tsukuba University School of Medicine in 1993
2007 Graduated from Toin Yokohama University Law School
Registered as a lawyer in 2010, specially appointed associate professor at Kanazawa University Hospital
Incumbent since 2015
There have been a series of cases in which it was too late for cancer patients to receive appropriate treatment due to oversight of CT and other test results by the attending physician and lack of communication with radiologists. It is said that the hospital information system is becoming more complicated in the background, and countermeasures are required. We asked Mr. Junko Echigo, Director of the Medical Safety Department (Health Quality and Safety Measures Office) of Toranomon Hospital, who has a double license of a doctor and a lawyer, about the tendency of medical safety accidents in recent hospitals and the points of countermeasures.

In 1999, an accident was discovered in which a patient was mistaken for surgery at a hospital, which became a major problem. At that time, preanesthetic administration was performed, but recently, there are many cases where the patient is awake and walked into the operating room. Information) and other information are put on the wristband, and measures against misidentification such as identity verification are taken, and such mistakes are significantly reduced. In addition, mistakes such as making a wrong diagnosis by mistaken the sample were also seen before, but it seems that it has decreased by collation confirmation by introducing an automatic recognition system.
According to Echigo, the recent trend toward medical accidents is also influenced by the complexity of hospital information systems. This is the case when the attending physician overlooks a report that points out suspicion of cancer in so-called hospital diagnostic imaging. The Japan Council for Quality Health Care alerted hospitals nationwide in May this year, saying that there were 37 oversights due to lack of confirmation in 2015-18.
"In the case of paper medical records, test result data or diagnostic imaging reports are stored in a file, so there were few cases where they were overlooked, but the spread of electronic medical records and the like had a major impact on a series of overlooked cases. "There is," Echigo points out.
As for the flow of CT examination, the attending physician first places an examination order, the radiologist performs the examination, creates an image, and prepares a diagnostic report. The submission will be carried over to the day after the inspection to read hundreds of images and compile the report. On the other hand, in an electronic medical record, the captured image itself arrives at the terminal of the attending physician immediately, so that the attending physician often makes a diagnosis only by looking at the image before the report arrives. Your doctor tends to focus only on your area of expertise and not on the surrounding organs. In some cases, the report received after that is not confirmed, and as a result, cancer is overlooked.
To prevent such mistakes, Mr. Echigo says, "It is desirable to create a mechanism on the electronic medical record to check whether the attending physician has confirmed the diagnostic imaging report." However, it is complicated and complicated, such as from different system vendors, and if there are many parts to be customized, the cost will increase, but the current situation is that it does not always function effectively.
On the other hand, the current situation that there is a shortage of radiological diagnostic specialists who diagnose images also complicates the problem. Even in large hospitals, there are many cases where there are only a few full-time radiologists, but the need for diagnostic imaging is increasing, and the amount of work is increasing year by year. For example, the number of CT scans may be hundreds, and you have to see thousands to 10,000 images a day. "It is extremely difficult to completely check all images, and although the burden of interpretation may be reduced if artificial intelligence develops, the final decision must be made by the doctor. There is no change in the situation where it does not happen, and quality control is becoming more difficult, "says Echigo.
Focusing on the serious medical accident that killed a patient at a university hospital, the national government is also working on safety measures for the hospital. In other words, it is a review of approval requirements for special function hospitals and cancer treatment cooperation base hospitals.
The review of approval requirements for special function hospitals has been applied since 2016 for "assignment of medical safety managers", "mandatory reporting of accidents", "clarification of introduction process for new high-difficulty medical technologies", etc. ing. Furthermore, with the aim of strengthening governance in a well-organized organizational structure, it will be obligatory to clarify the method and authority for appointing hospital directors, and to set up a meeting where multiple occupations participate to discuss hospital management.
In addition, the establishment of a "medical safety management department" will be obligatory as a designated requirement for cancer treatment cooperation base hospitals after 2019. Full-time doctors, pharmacists, and nurses will need to be assigned to the medical safety management department that requires a new installation.
On the other hand, in the 2018 medical fee revision, "Medical Safety Measures Regional Cooperation Addition 1" (50 points) and "Medical Safety Measures Regional Cooperation Addition 2" (20 points) are newly established as additions to the "Medical Safety Measures Addition". It was done (figure). It is necessary to assign a full-time doctor to medical institutions other than hospitals with special functions, but multiple medical institutions cooperate to "evaluate medical safety measures" at least once a year.
Mr. Echigo said, "It is important to provide incentives, which will lead to the advancement of standardization of medical safety in Japan."
figure
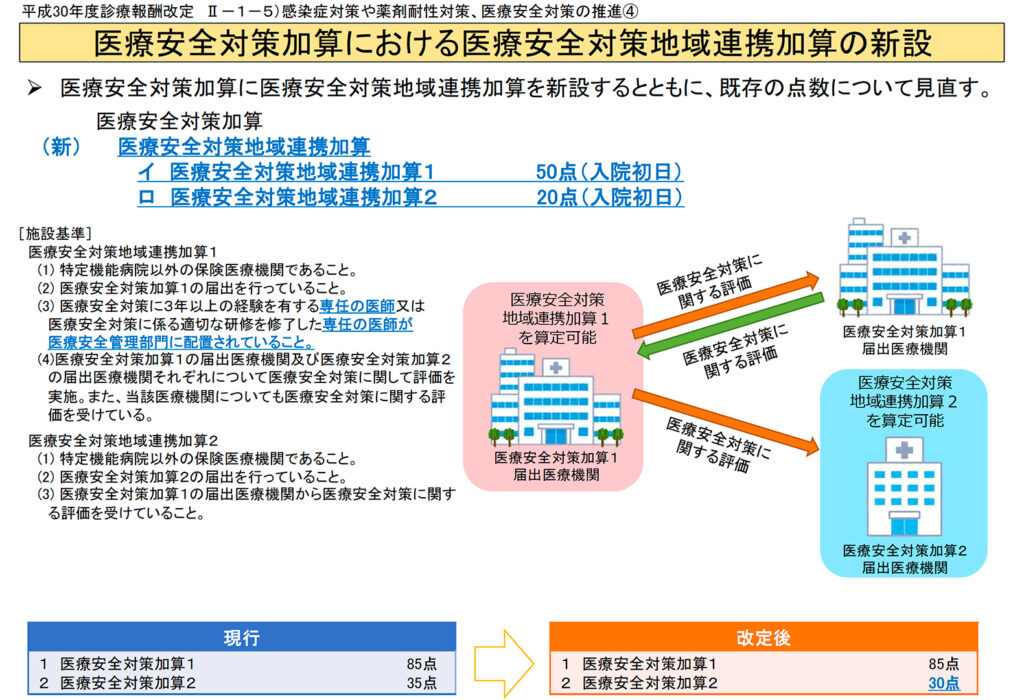 Source: From the 2018 medical fee revision (Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare)
Source: From the 2018 medical fee revision (Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare)
So how should we proceed with hospital safety measures? In general, education and training for hospital staff and thorough operation of manuals for medical safety are carried out, but Mr. Echigo said, "In a large hospital, about 10% of the staff change every year, but the people who have moved are the current ones. The hurdles for putting it on the rules are high. In addition, there are many cases where there is a temperature difference between employees in their awareness of medical safety. "
It is desirable that all staff members be united under the leadership of the hospital director to raise awareness of medical safety. For that purpose, it is effective to set clear goals, which can be the basis for hospitals and staff to work together on medical safety.
Regarding medical safety measures, in addition to system measures, efforts to improve safety in terms of medical technology are also required. Mr. Echigo points out, "It is hoped that various simulation models will be used to create opportunities for various skill training and simulation training for residents and comedics." The Federation of National Public Service Personnel Mutual Aid Associations, which operates 34 hospitals nationwide, has established a simulation lab center in the Toranomon Hospital Branch (Kawasaki City, Kanagawa Prefecture) with the aim of improving the quality and safety of medical care.
At the center, a resident lab manager plays a central role in conducting various trainings for new residents, nurses, and comedical staff using a standardized simulator of elementary medical techniques as a training instructor, as well as all medical engagement. We will provide life-saving resuscitation training and training on new techniques to avoid danger to people. We also provide training for instructors and risk managers.
The training contents by simulation are primary first aid, AED, secondary first aid, airway management / tracheal intubation, respiratory / circulatory training, intravenous injection / blood sampling, CV catheter insertion method, suture / disinfection method / banding method, electrocardiography, ultrasonography. A wide range of on-the-job training such as ultrasonography, lumbar intubation, and abdominal endoscopy training box is possible.
Mr. Echigo covers from accident prevention to response in the event of an accident to subsequent disputes with Seams, and also handles proceedings held at hospitals as an agent. In the first half of the 2000s, the number of medical litigation increased to more than 1,100, but then gradually decreased, and about 800 cases have been filed annually since 2008. It may be because the number of projects is decreasing. "