Release date: 2021.07.30
Mutant strains of the new coronavirus called the delta strain are spreading rapidly around the world, but why does the new coronavirus repeatedly mutate as it spreads from person to person? Also, how do mutations change the nature of the virus? I will summarize the mechanism of mutation of the new coronavirus.
Viruses are said to change their genes in order to adapt to the changing environment in nature as a survival strategy. Unlike bacteria, viruses cannot multiply on their own, so they invade the cells of other organisms, such as humans and animals, and reproduce by making copies of themselves. At this time, a large number of viral genes are copied.
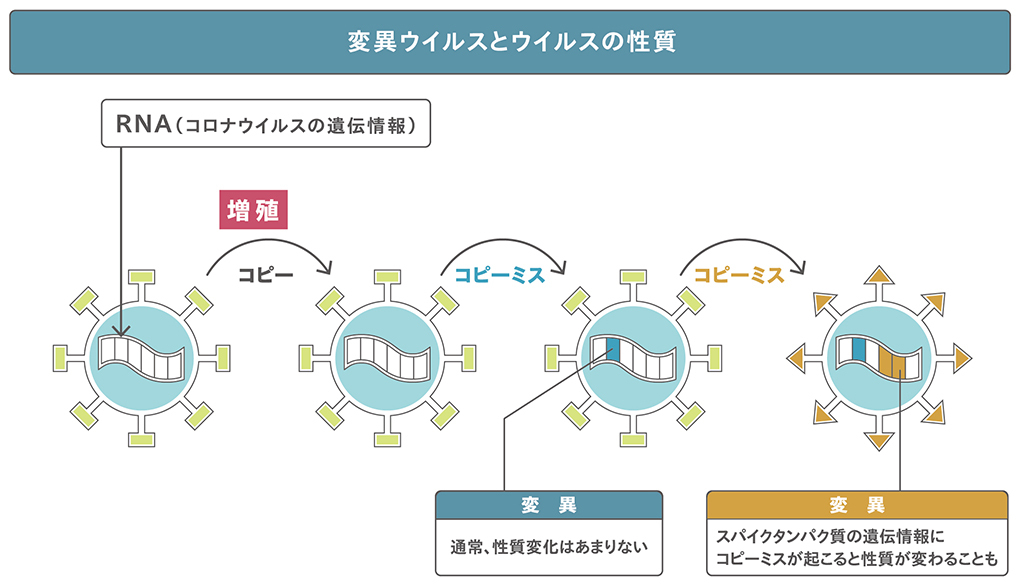
In the case of the new coronavirus, as it repeats copying many times, a very small mistake occurs in the sequence of a substance called RNA, which is responsible for genetic information. This copy mistake, so-called change in genetic information, is called "mutation". When the letters of RNA are rewritten, the amino acid groups specified there change, and the shape of the protein may change. The virus gradually mutates as it spreads from person to person. This mutated virus is a mutant strain. It is known that the new coronavirus undergoes a small mutation at a frequency of about one location every two weeks. Compared to the new coronavirus discovered in Wuhan, China in January last year, it is estimated that the current coronavirus has about 20 to 30 mutations.
In Japan, the genetic information of the new coronavirus gradually changed while the infection was repeated, but even if it changed, it was a copy error of the genetic information that had little to do with the nature of the virus, so mutation strains became a problem in Japan. It wasn't long before I became a . A more contagious mutant alpha strain of the virus was found in the UK last autumn, and it became a big problem.
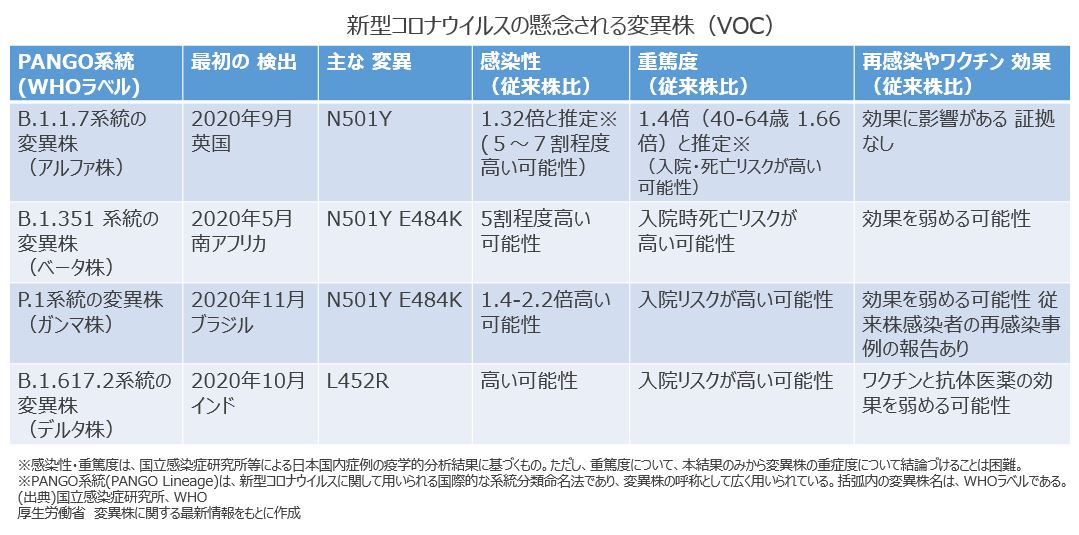
Even small mutations in important parts of the viral genetic code can change the nature of the virus. What these mutant strains have in common is that there is a mutation in the genetic information of the "spike protein" part of the virus. This spike protein is an extremely important site that serves as a scaffold when the new coronavirus infects human cells, and its properties may change due to mutation. There are three issues in particular: (1) Ease of spread of infection (transmissibility): Due to the mutation, it binds more tightly to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor on the surface of human cells, resulting in increased infectivity compared to conventional strains. (2) Severity of the disease caused (virulence): It is said that there is a possibility that the risk of hospitalization or death at hospitalization is high. (3) Attenuation of vaccine effect (immune escape): It has been shown that some mutant strains may weaken the vaccine effect.
When a strong mutation stocks of infection comes into the country, the percentage of infected with the mutation stocks gradually increases, and eventually most of them will be replaced. In Japan, the first conventional virus (China/Wuhan type) that entered the country spread, but a highly contagious alpha strain came in from overseas and replaced it. And now it is being replaced by the Delta strain, which is even more infectious. Genetic information has changed so that the virus can easily multiply, so in a sense it can be said to be the "evolution" of the virus.
Influenza viruses also undergo repeated minor mutations, but once every several decades, they undergo a full model change. With this full model change, the avian influenza virus, which had previously infected only birds, can now infect humans, and the new strain of influenza virus can now be transmitted from person to person.
Some experts say the new coronavirus could be even more contagious than the Delta strain. Mutant viruses appear due to copying mistakes during proliferation, so if you reduce the number of copies, you will reduce the chances of mutation. In other words, it is important to control the spread of infection, and it can be said that the importance of infection control is increasing.
MEDIUS Group is developing a business centered on the sale of medical equipment. We (Medical + us) involved in medical care also want to play the role of an information source (Media) that delivers useful information for the medical field and people's healthy tomorrow.