ASOURCE®NAVI

公開日:2023.08.08
虚血性心疾患(心筋梗塞・狭心症)の患者は70万人以上とされ、日本人の死因のうち約5%を占めるとされます。特に心筋梗塞は、心臓の筋肉(心筋)に血液を送る冠状動脈が完全に塞がった状態となり、突然死することもあります。虚血性心疾患の症状や診断のための検査法、早期発見のための対策などについてまとめます。
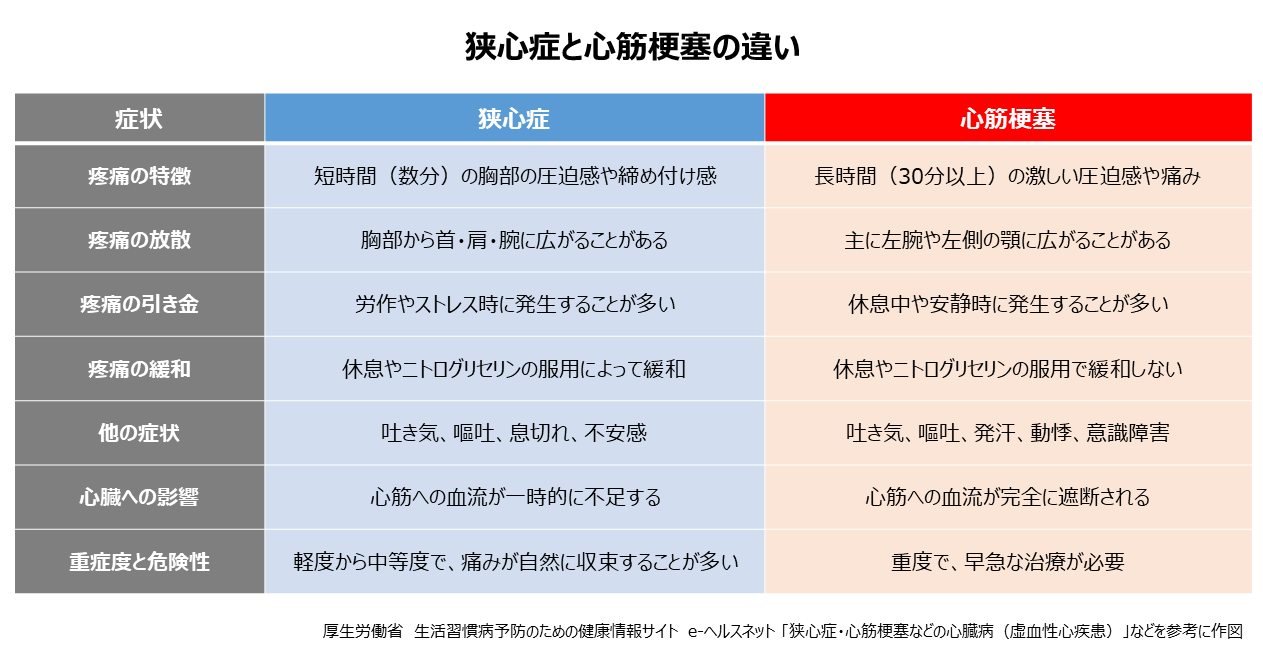
心筋に血液を送る冠状動脈が狭くなったり、塞がったりして、心筋への血液の流れが悪くなり、心筋が酸素不足に陥る状態を虚血性心疾患と呼びます。冠動脈が狭くなった状態が狭心症、塞がった状態が心筋梗塞です。厚生労働省の行った患者調査によると、虚血性心疾患の患者数は約72万人(2017年時点)で、男性と女性を比べると男性患者数が多い状況です。また、日本人の死因のうち約5%を占めるとされます。虚血性心疾患の主要な原因は動脈硬化で、高血圧、脂質異常症、糖尿病などや、運動不足、喫煙などの生活習慣によって起こりやすいといわれます。
狭心症は、冠状動脈が狭くなってはいますが完全には途絶されていませんので、心筋細胞が壊死することはなく、すぐに生命が脅かされることは多くありませんが、軽い労作でも胸を締めつけられるような強い痛みや圧迫感の症状が現れるようになると、心筋梗塞の前兆であることがほとんどです。発症していても患者本人が気づかない場合もあります。特に高齢者の場合は、加齢によるものと症状を見過ごしてしまうケースも多いようです。また、糖尿病を患っている人も、合併症のひとつである神経障害の影響で、狭心症の痛みを感じにくくなり、見過ごしてしまうケースがあります。狭心症の多くはなんらかの動作中に起こることが多いのですが、安静時に冠状動脈の痙攣が起こり、狭心症の発作が起こる場合もあります。
心筋梗塞は、冠状動脈が塞がった状態で、心筋に酸素が行き届かなくなり、突然死することもあります。心筋梗塞の年間死亡者数は3万人以上といわれ、日本人の3大死因の1つです。発症すると冷や汗・吐き気を伴う強い胸の痛み・圧迫感などの症状が出ます。胸の痛みは30分以上続きます。心筋梗塞を一度発症すると、死亡率は30%にものぼるといわれます。
虚血性心疾患の 一般的な症状には、胸痛や圧迫感、吐き気、息切れのほかにも、脇腹の痛み、腕や肩の痛みなどがあります。特に、胸の苦しさや痛みを感じる症状が現れた場合は、早めに医療機関を受診することが大切です。
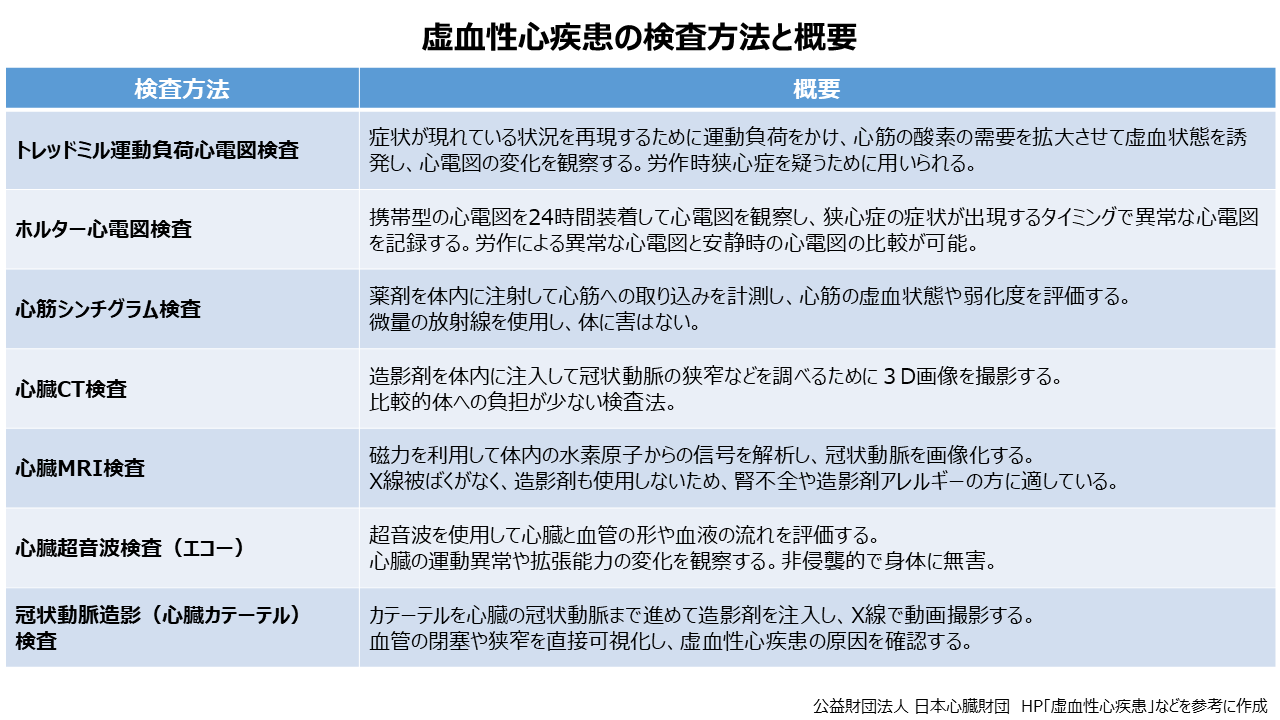
虚血性心疾患を早めに見つけるための検査法としては以下のものがあります。
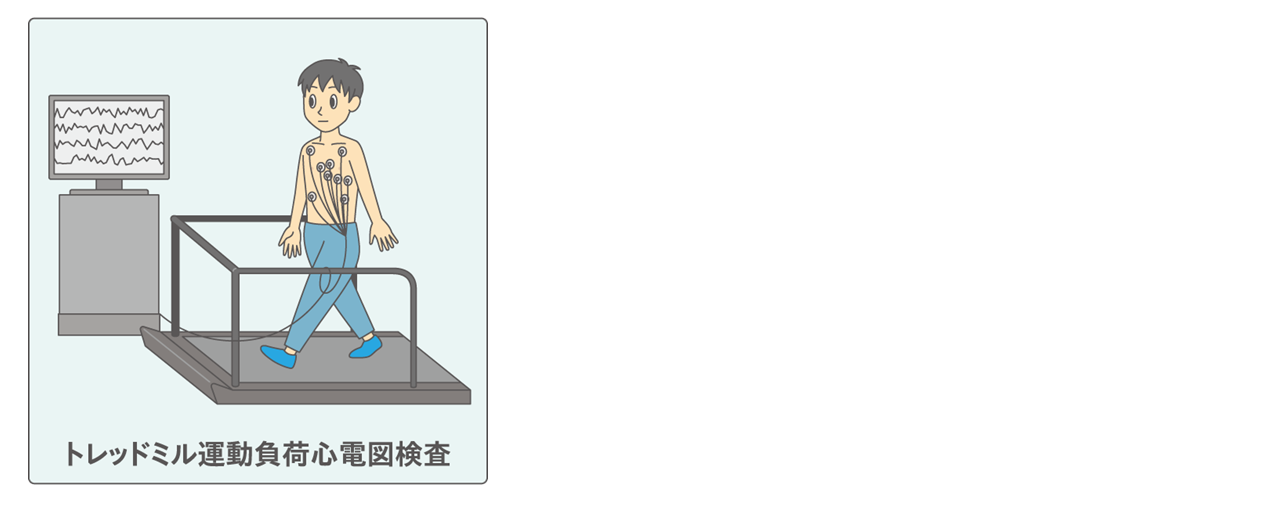
①トレッドミル運動負荷心電図検査:
症状の現れていない時に心電図を確認しても変化がありません。そこで、症状が現れている状況を再現するために運動の負荷をかけ、心筋の酸素の需要を高めて虚血状態を誘発し、その際の心電図の変化を観察します。負荷は動くベルトコンベアーの上を歩行することで行い、運動負荷をかける前後の心電図と合わせて、運動中の心電図、血圧を確認します。この検査で、心電図に異変が見られた場合には、労作時狭心症を疑います。
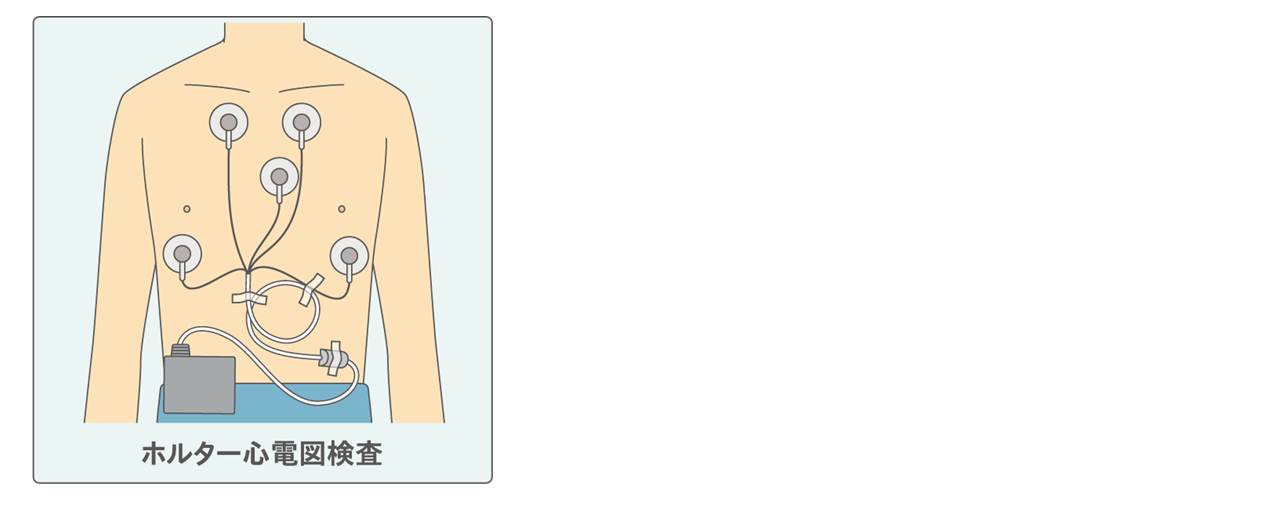
②ホルター心電図検査:
狭心症の症状は数分で消失してしまうため、症状が出現した際の心電図がとりづらいという難点があります。そこで、持ち運びができる携帯型の心電図を24時間装着して観察することで、どのタイミングで異常な心電図が出るかを調べます。異常な心電図が出たのが労作によるものなのか、安静時に起こっていたものかの判別が可能です。
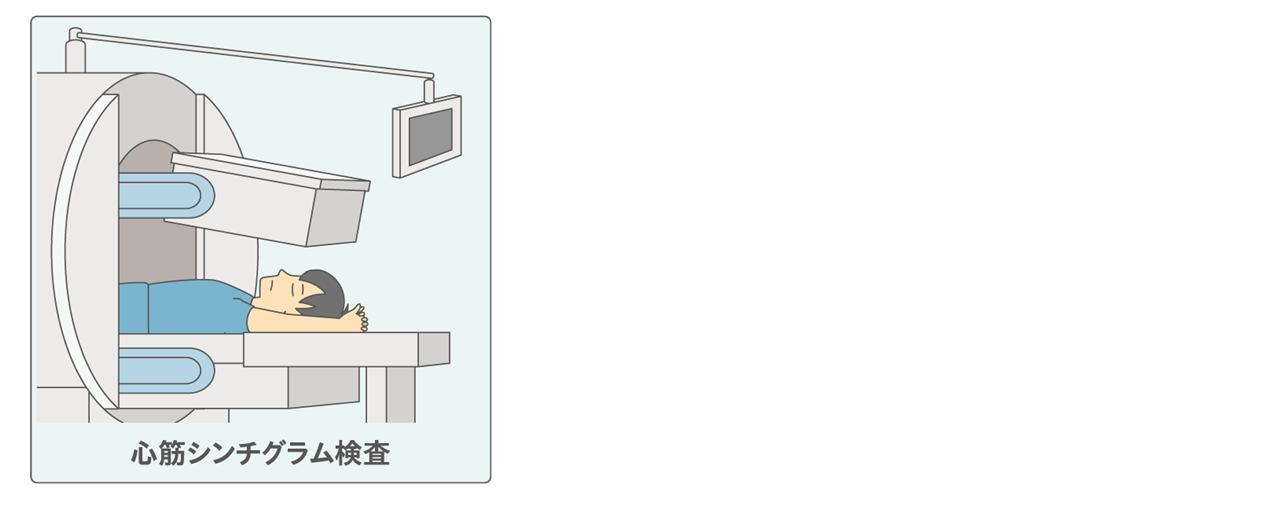
③心筋シンチグラム検査:
放射線を微量に発生する薬剤を体内に注射して心筋への取り込みを計測します。心筋がどれくらい虚血状態なのか、また心筋がどれくらい弱ってしまっているかの評価ができます。使用される薬剤は半日ほどで自然に消失するほど微量なので、体に害が出ることはありません。
④心臓CT検査:
造影剤を体内に注入して撮影し、3D画像で冠状動脈の狭窄などを調べます。従来の主流であった心臓カテーテル検査と比べて、体の負担が少ない検査です。ただし、造影剤は腎臓を通って尿として排泄されるため、腎機能に異常がある方は注意が必要です。
⑤心臓MRI検査:
磁力を利用して体の水素原子からの信号をコンピュータ解析して冠状動脈を画像化します。X線被ばくがないほか、造影剤も使わず検査できるため、腎不全や造影剤アレルギーの方に適しています。
⑥心臓超音波検査(エコー):
胸のちょうど心臓のところに超音波を当てて画像を映し出します。心臓を輪切りにして心臓や血管の形・血液の流れを調べます。心臓の運動異常や拡張能力の変化が観察されることがあります。超音波は身体に無害で痛みもありません。
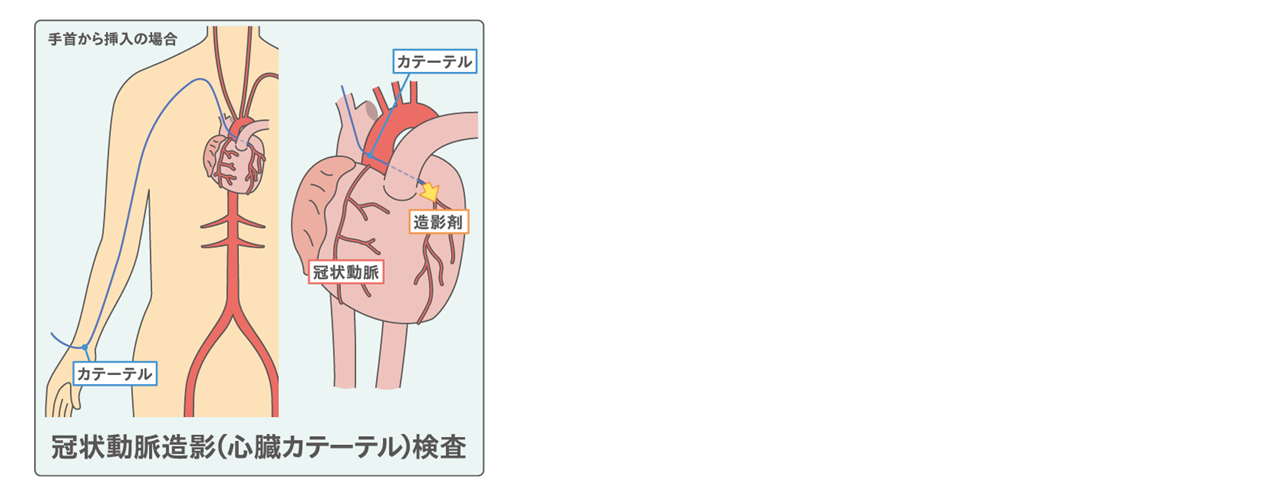
⑦冠状動脈造影(心臓カテーテル)検査:
足の付け根や手首から直径1〜3mm、長さ1mのカテーテルという細くやわらかい管を挿入し、心臓の冠状動脈まで進めて造影剤を注入し、X線で動画撮影します。侵襲的な手法ですが、虚血性心疾患の原因となる血管の閉塞や狭窄を直接可視化することができます。また、検査で冠状動脈が細くなっている部分が見つかった場合は、そのまま動脈を拡げる治療が行われることもあります。
虚血性心疾患が疑われた場合は、心電図検査、画像診断と検査を進め、さらに冠状動脈造影検査を行ったりします。日本人の死因の第一位が悪性新生物<癌>で、続く第2位が心疾患(心不全、虚血性心疾患)です。重要なのは、心筋梗塞を起こす前に狭心症の段階で早期発見することです。もし体に違和感を覚えたら、早めの受診をお勧めします。
メディアスグループは、医療機器の販売を中心とした事業を展開しています。医療に携わる私たち(Medical+us)は、医療現場や人々の健康的な明日へ役立つ情報をお届けする情報発信源(Media)の役割も果たしていきたいと考えています。