
Release date: 2023.06.22
Japan's medical insurance system is characterized by a high degree of fulfillment and quality of medical services based on a universal health insurance system, and is highly evaluated internationally. We will summarize the structure and characteristics of this system and a comparison with overseas systems.
Japan's medical insurance system is a universal health insurance system, and all citizens, from infants to the elderly, are enrolled. There are three types of insurance: (1) National Health Insurance (regional insurance) for self-employed people, farmers, and unemployed people; (2) Employees' insurance (occupational insurance); It is classified into three. (2) “employee insurance” includes “Japan Health Insurance Association-managed health insurance (Kyokai Kenpo)” mainly for employees of small and medium-sized enterprises, and “union-managed health insurance (health insurance)” mainly for employees of large companies. Unions), and Mutual Aid Associations for national and local government employees, private school teachers, etc., and employers bear part of the insurance premiums.
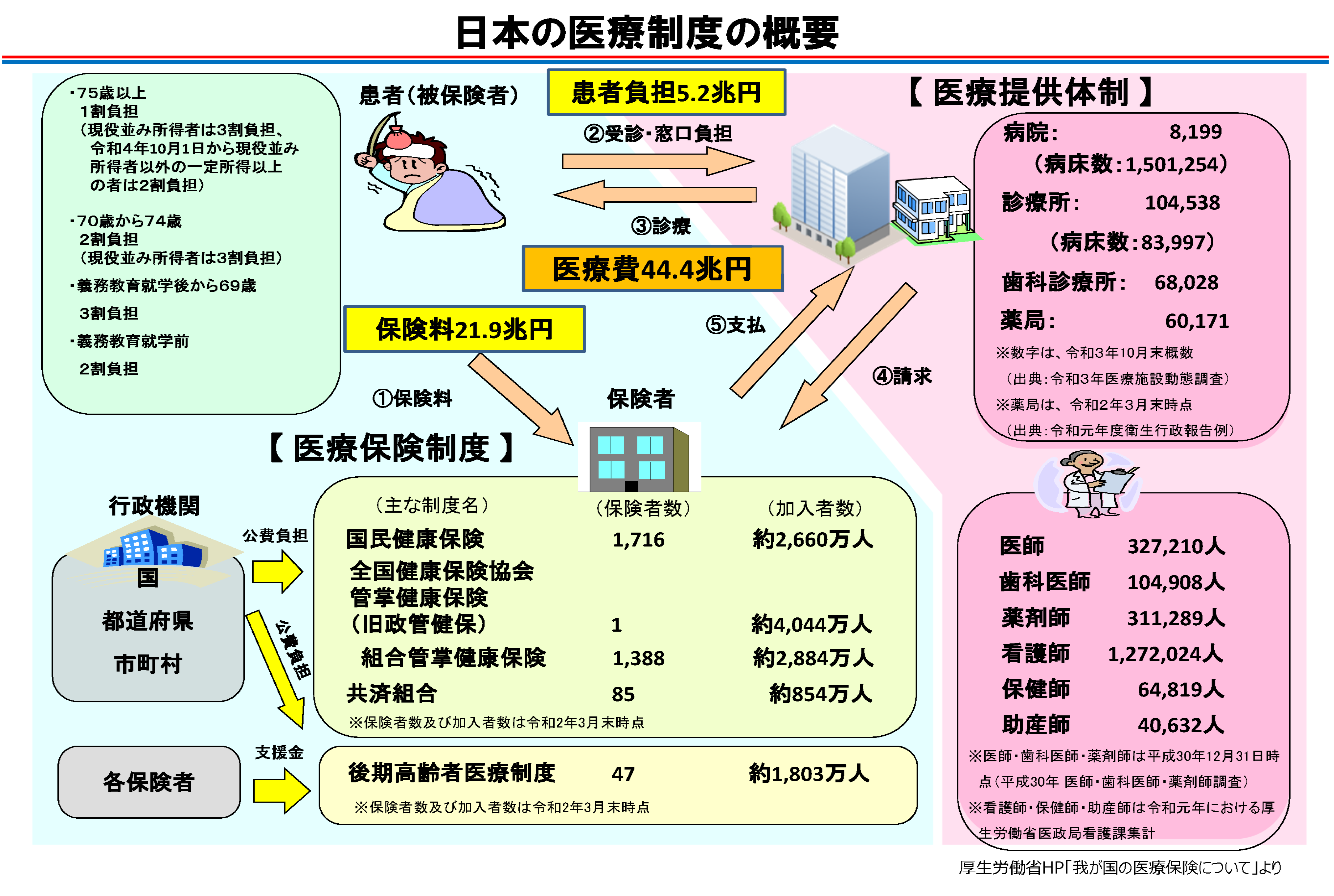
By paying a fixed amount of premiums each month, the insured person pays 10% to 30% of the medical expenses related to the medical treatment at the insurance medical institution when receiving medical treatment for illness or injury. (30% for employees' health insurance, 30% to 20% for national health insurance, and 10% for medical care system for the elderly aged 75 or over). After the medical treatment, the insured medical institution, etc. requests the insurer to pay the amount after deducting the insured person's co-payment from the medical expenses related to the medical treatment. Funding sources for national medical expenses include insurance premiums and copayments of insured persons, as well as public expenditures.
Medical services and prices are regulated by a medical fee point table. Medical insurance covers not only the treatment of illnesses and injuries, but also the costs of routine immunizations and medical examinations. In addition, in order to prevent the financial burden of medical expenses from becoming heavy, if the medical expenses paid at insurance medical institutions or insurance pharmacies exceed the upper limit in one month, the amount exceeding the upper limit will be paid. I have. The upper limit is determined according to age and income. In this way, the people are prevented from becoming financially destitute due to the burden of medical expenses.
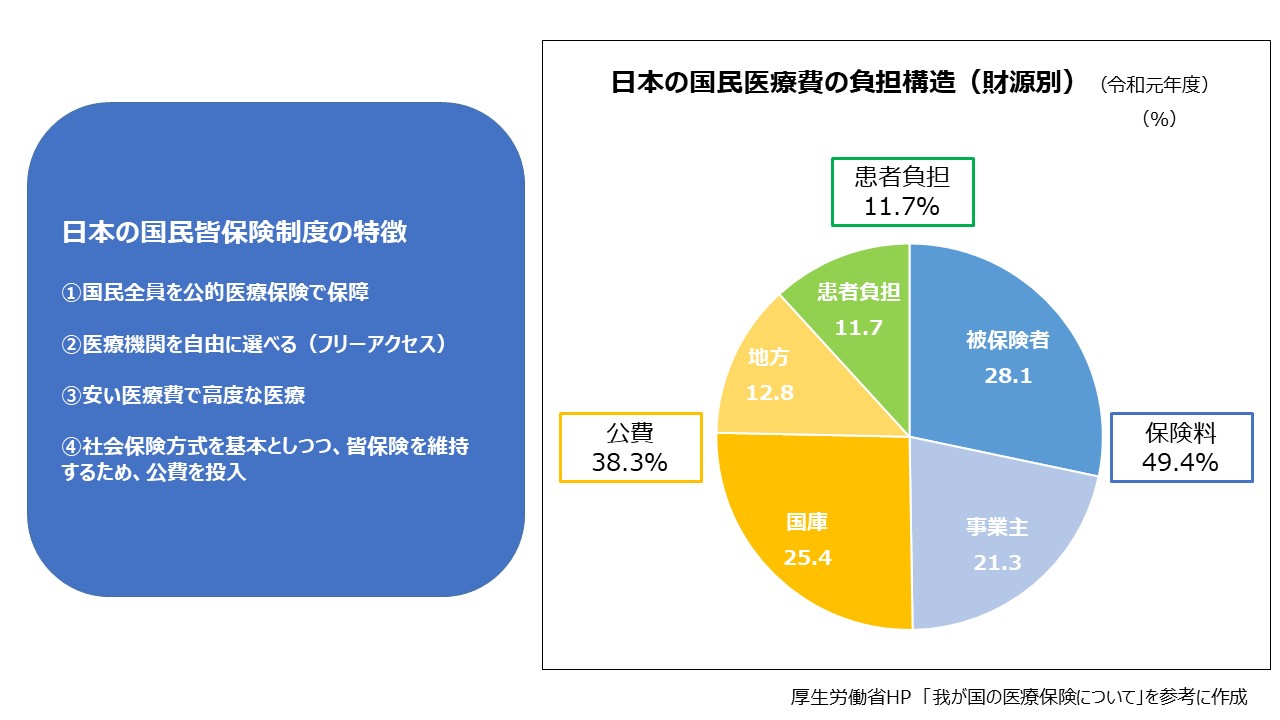
A feature of Japan's medical insurance system is that all citizens are covered by public medical insurance. If you have your health insurance card, you can freely receive medical care using public insurance at any medical institution at any time. In addition, advanced medical care is provided at a low medical cost and public funds are invested.
Then, what kind of medical system is there overseas? Introducing the UK, France and the USA.
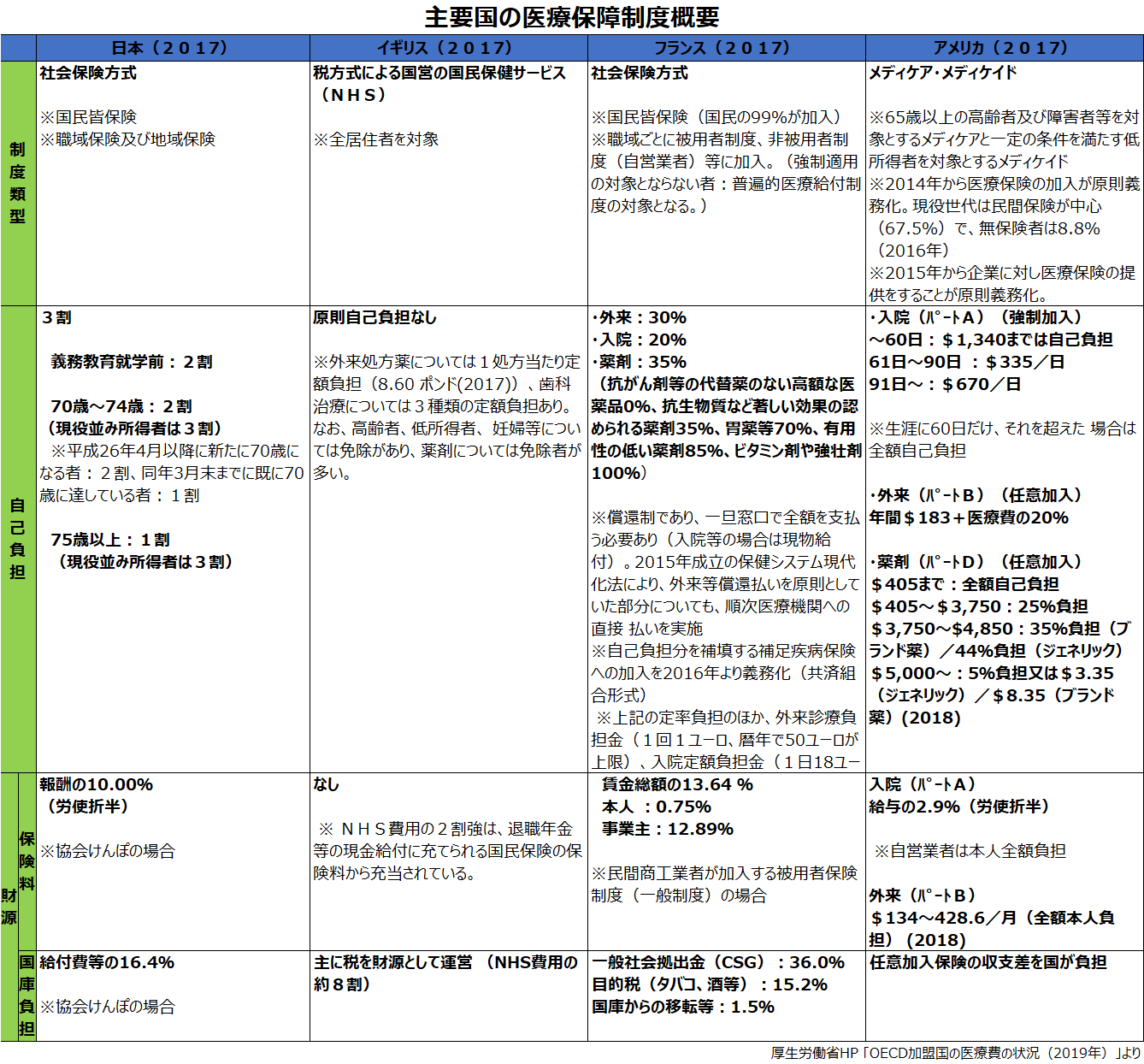
In the UK, there is a public health system, the National Health Service (NHS), which is funded by taxes and national insurance premiums, and in principle medical care is provided free of charge. For this reason, health care is also provided to poor and low-income people. Also, if you have a physical disorder, regardless of the part or type, first see a local family medical institution called a GP (General Practitioner), and if necessary, visit a specialized hospital. and university hospitals. In this way, the division of roles between medical institutions improves their expertise and efficiency, and has the advantage of delivering the necessary medical care to those who need it. is also provided. On the other hand, there are cases in which a patient is forced to wait two to three weeks to see a family doctor, or is diagnosed as needing to see a specialist, and even if he or she makes an appointment with a specialist with a letter of referral, there are cases where the patient is forced to wait several months before seeing a doctor. It is said that it is not uncommon.
In France, there is a universal insurance system, and the copayment is 30%. Patients are free to choose the doctor and hospital they want, but if they visit a specialist instead of going through their family doctor, they will have to pay 70% of the cost.
On the other hand, in the United States, there are many world-famous medical institutions and specialist doctors, and high-level specialized medical care is provided, but only the elderly, disabled, and low-income people can enroll in the public medical insurance system. , Other citizens must enroll in private medical insurance or pay their own medical expenses. Premiums for private medical insurance vary according to age, occupation, and health condition, but due to the high premiums, many people cannot enroll. In addition, not all medical expenses are covered, and the out-of-pocket costs may be high. The general initial consultation fee is said to cost between $150 and $300. As a result, many people in the United States are unable to visit medical institutions for financial reasons, and the burden of medical expenses has become a major social problem.
When comparing treatment costs with other countries, the cost varies depending on the department, medical institution, length of stay, and treatment method, but in general, the cost of appendicitis treatment is about 1.08 million yen in France and about 940,000 yen in the UK. ~1,350,000 yen, approximately 740,000 yen in the US, and approximately 600,000 yen in Japan, depending on the country.
In this way, access to medical institutions and the method of determining medical expenses differ between Japan and other countries, but there are various mechanisms such as Japan's universal health insurance system, free access to medical care, and the high-cost medical care benefit system. It is comparable to other countries. However, medical expenses in Japan are increasing rapidly due to the aging of the population and advances in medical technology. As a result, Japan's medical system is in a severe financial situation. In order for this system to continue in the future, reforming the system and securing financial resources are issues.
MEDIUS Group is developing a business centered on the sale of medical equipment. We (Medical + us) involved in medical care also want to play the role of an information source (Media) that delivers useful information for the medical field and people's healthy tomorrow.