ASOURCE®NAVI
公開日:2023.12.26
骨髄移植は、生命をつなぐ役割を担う医療プロセスであり、多くの人々の命を救う可能性を秘めています。そこで、骨髄移植の仕組みを2回にわたってまとめます。第2回目は、ドナーからの骨髄採取、治療の流れ、海外の現状、今後の課題について紹介します。
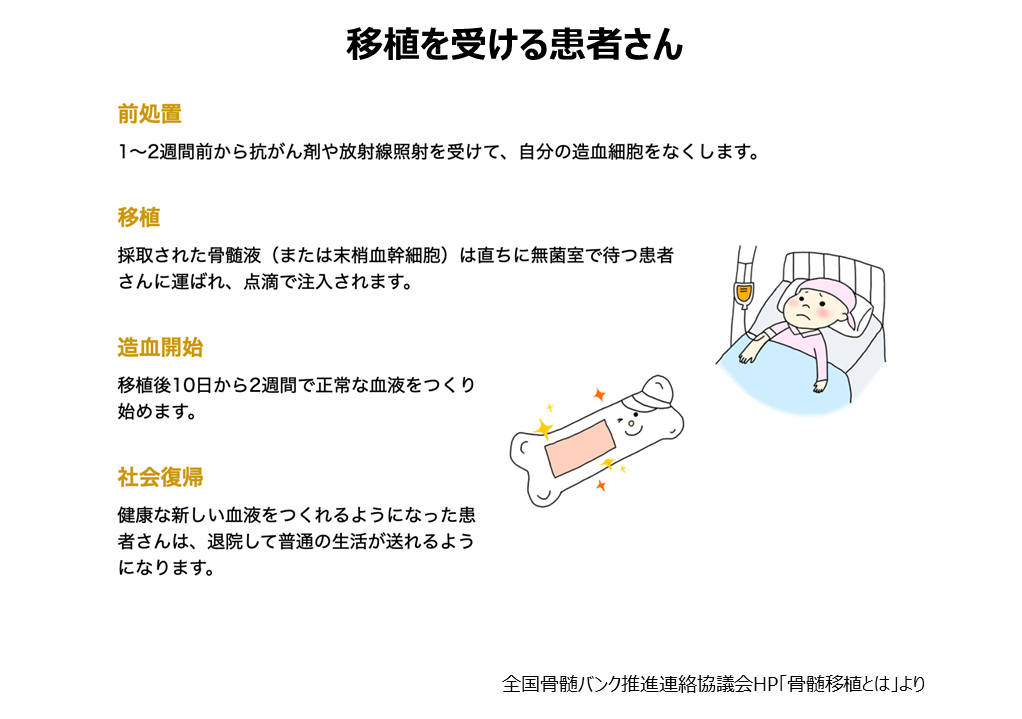
移植希望患者とHLA(白血球の型)が適合しドナーになると、確認検査や最終同意面談、骨髄や血液の採取前健診、採取のための入院、採取後健診などに10日間程度が必要になります。提供には、ドナー本人の意思だけでなくご家族の同意も必要としています。採取は、全身麻酔下で骨盤を形成する腸骨(腰の骨)から注射器により採取されます。手術室でうつ伏せ状態で、腸骨に針を左右数カ所刺して吸引します。採取する骨髄液の量は通常500~1,000mlで採取に要する時間は1~3時間です。入院費や交通費のドナーの負担はありませんが、休業補償はありません。官公庁や一部企業などで「骨髄ドナー特別休暇制度」を導入しているところもあります。また、自治体によっては、骨髄または末梢血幹細胞の提供を完了した人に対して奨励金を交付しています。

人体には免疫力(自身以外のものを異物とみなし排除する力)が備わっており、何もせずに骨髄移植を実施すれば、患者の免疫力により生着不全が起こります。そのため、骨髄移植時には患者自身の免疫を低下させる必要があり、移植当日の1〜2週間前から自分の造血幹細胞をなくすために抗がん剤、放射線治療(移植前処置治療)をします。移植当日はドナーから採取しておいた造血幹細胞(骨髄の中で血球を作り出すもとになっている細胞)を静脈より投与します。移植から約1ヶ月〜数ヶ月でドナーの血液に置き換わります。移植後に免疫細胞が患者を攻撃するリスクがあり、その場合は、ステロイド剤や免疫抑制剤で対処します。
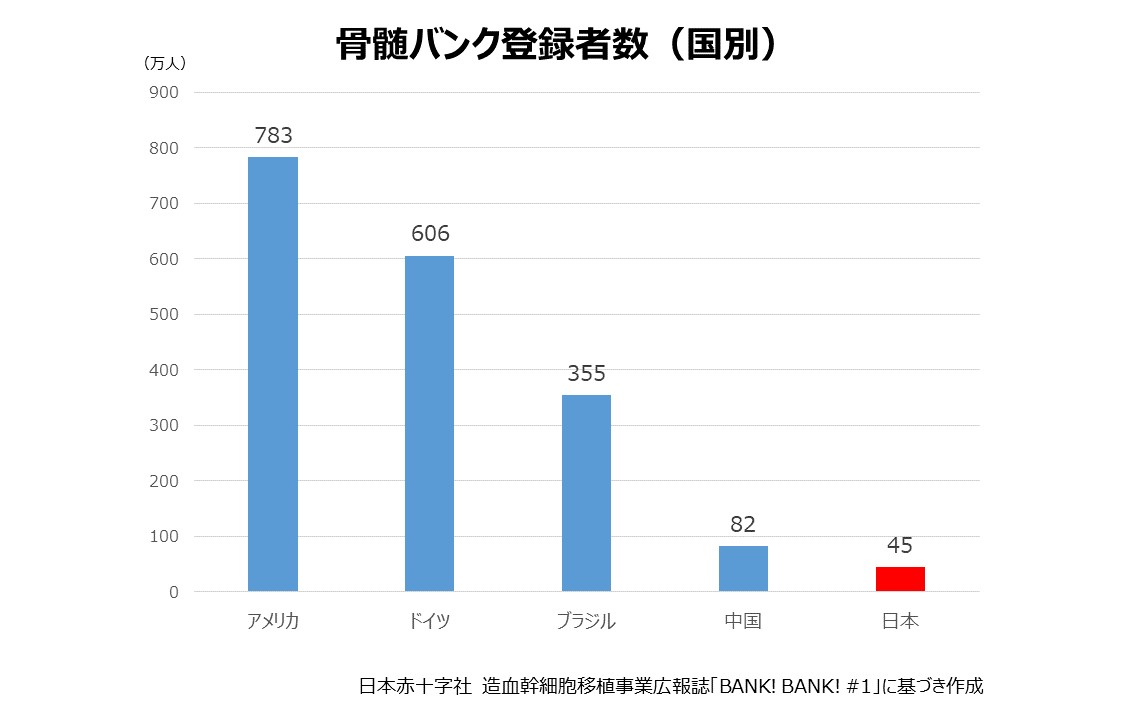
骨髄バンクの登録者数は2015年11月時点で日本は約45万人ですが、世界各国では、米国783万人、ドイツ606万人、ブラジル355万人、中国82万人(2015年5月時点のBone Marrow Donor Worldwideウェブサイト)となっており、海外と比較しても少ない現状です。
造血幹細胞を移植する方法は、骨髄移植のほかに末梢血幹細胞移植があります。末梢血(全身を流れる血液)には通常、造血幹細胞はほとんど存在しませんが、白血球を増やす薬を注射すると、末梢血中にも流れ出します。採取前の3~4日間、ドナーに連日注射し造血幹細胞が増えたところで、血液成分を分離する機器を使い造血幹細胞を採取し、骨髄移植と同様の方法で患者さんに注入します。
ドナー登録者は年齢とともに減少傾向にあり、骨髄バンクドナー登録者で最も多い年齢層は、令和4年3月末時点で49歳(10年前は39歳)となっており、高齢化が進んでいます。若い世代のドナー登録を増やすことが喫緊の課題です。また、骨髄移植は、患者の生命を救う効果的な治療法ですが、移植後のQOL(生活の質)の低下が問題となっています。移植後の合併症や治療による副作用により、患者は体力や免疫力の低下、疲労感、倦怠感などの症状に悩まされることがあります。移植後のQOLの向上には、患者の体力や免疫力の回復を促す治療や、患者の心理的・社会的支援が重要とされます。
メディアスグループは、医療機器の販売を中心とした事業を展開しています。医療に携わる私たち(Medical+us)は、医療現場や人々の健康的な明日へ役立つ情報をお届けする情報発信源(Media)の役割も果たしていきたいと考えています。