
Release date: 2023.10.30
Even today, with the advances in medical science, blood cannot be produced artificially. Blood for transfusion is essential for treating illnesses and injuries, and it is supported by people's daily blood donations. Therefore, we will introduce the mechanism of blood donation and blood transfusion.
Blood donations are primarily used as transfusions to treat sick or injured patients. It maintains life by supplying fresh blood to patients who have lost a large amount of blood due to disasters, accidents, surgeries, etc. Blood transfusions are also required to treat cancer, leukemia, anemia, and diseases of the digestive and circulatory systems. Furthermore, blood transfusions are essential for dealing with complications during childbirth and premature infants.
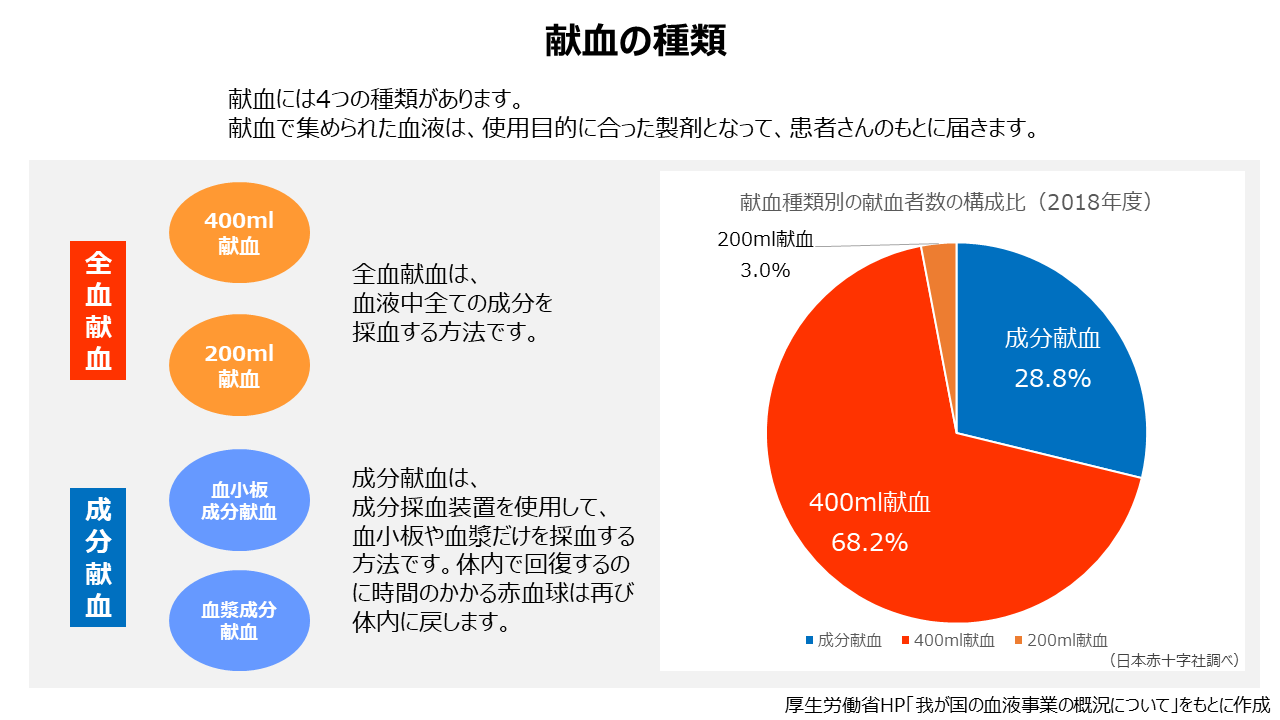
There are restrictions on the age at which blood can be donated, generally from 16 to 69 years old. There are two types of blood donation: whole blood donation and component blood donation. Whole blood donation includes 400mL blood donation and 200mL blood donation, and all components of blood are donated. Although 200ml blood donation may be applicable depending on the recipient's condition such as health condition and weight, 400ml blood donation is recommended in most cases. This is because patients may experience side effects from transfusing multiple blood types, even if they are of the same blood type. To minimize this, it is desirable to use blood from a smaller number of people. On the other hand, component blood donation includes platelet component donation and plasma component blood donation, in which only specific components such as platelets and plasma are collected using a blood component collection device, and the red blood cells, which take time to recover in the body, are reintroduced into the body. Here's how to get it back. Component blood collection has the advantage of being less stressful on the body, and allows for the donation of large amounts of plasma and platelets.
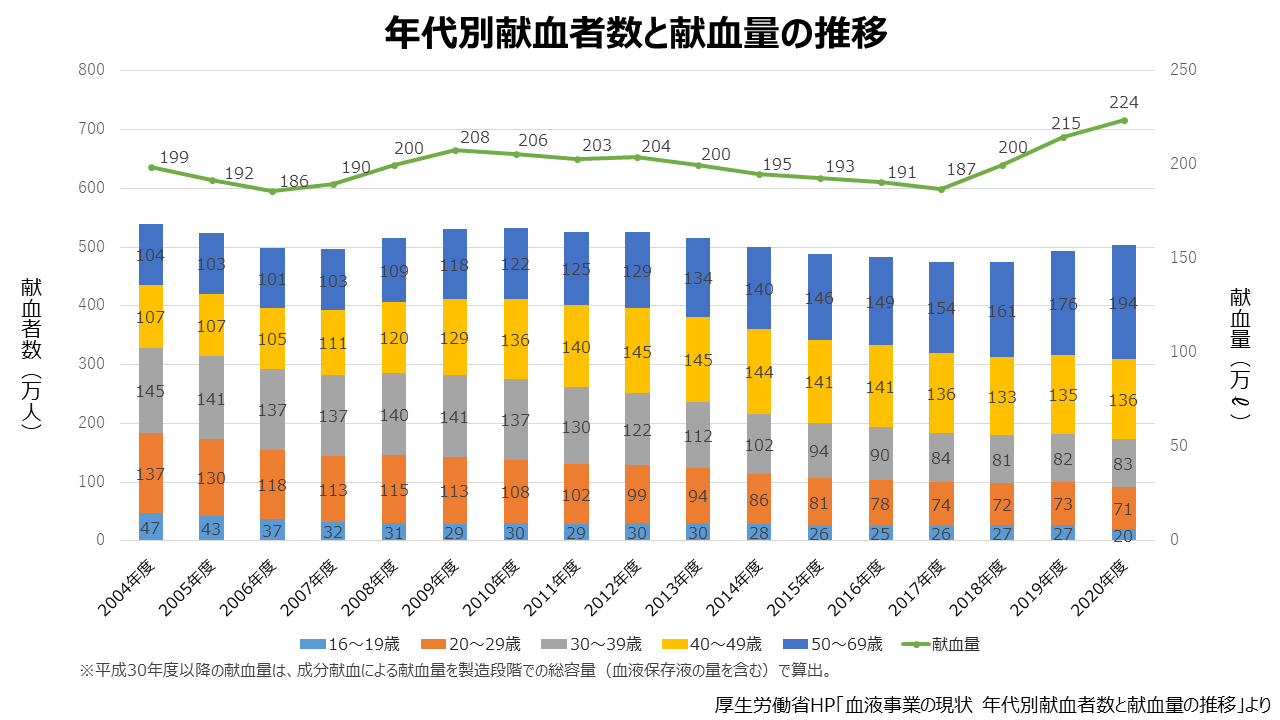
The number of blood donors is on the decline. According to the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare and the Japanese Red Cross Society, there were more than 6 million people a year in the 1990s, but the number decreased to about 4.73 million in 2017. Due to factors such as the declining birthrate and aging population, the number is decreasing, especially among young people.
Blood donated at blood donation rooms across the country is delivered to the Japanese Red Cross Society's block blood centers, where it is turned into blood products and delivered to medical institutions via prefectural Red Cross blood centers.
Blood donation also helps in the early detection of illness in the donor. Donated blood will be tested for syphilis, HTLV-1 (human T-cell leukemia virus type 1), hepatitis, etc., and if any abnormalities are found, those who request it will be notified.
Donated blood is delivered to medical institutions that need it and transfused to patients. The main processes are as follows.
① Collect blood from blood donors and perform necessary tests
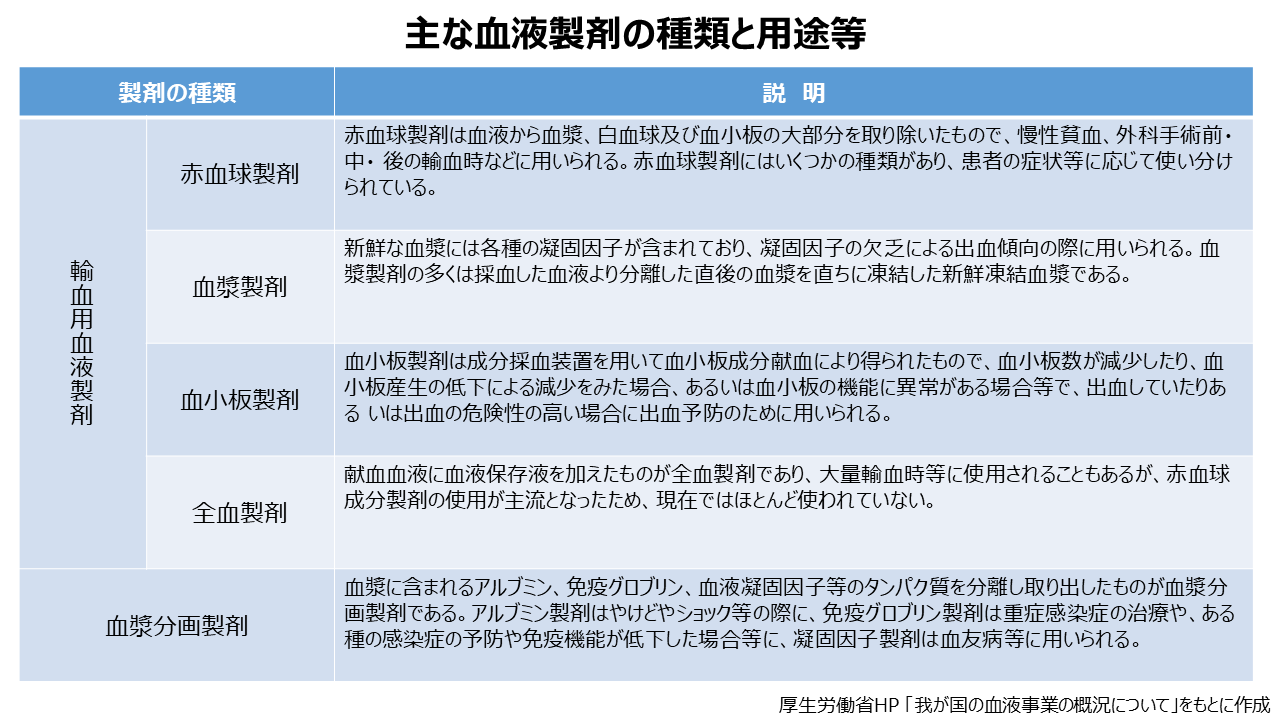
②The blood received from donations is separated into components, and red blood cells, platelets, fresh clotting factors, etc. are extracted.
③ Transfuse the necessary blood components according to the patient's situation.
Because blood contains living cells, it cannot be stored for long periods of time. The storage period for "red blood cells" is 28 days after blood collection (storage temperature 2-6℃), "platelets" for 4 days after blood collection (storage temperature 20-24℃), and "plasma" for 1 year after blood collection (storage temperature 20-24℃). (Storage temperature: -20℃ or below), and "whole blood" is stored for 21 days after blood collection (Storage temperature: 2-6℃).
Blood transfusions require the patient's consent, and it is possible for patients to refuse blood transfusions for religious reasons. For this reason, in February 2008, five related academic societies and other organizations jointly created the ``Guidelines for Religious Refusal of Blood Transfusions,'' which summarized how to respond in the field depending on the patient's age and situation. Currently, many medical institutions are implementing "relative blood transfusion therapy" (respecting the will of the patient and making every effort to provide non-blood transfusion treatment as much as possible) based on this guideline and according to the policy of the medical institution. Either the position or idea that blood transfusions should be performed when there is no life-saving means) or the ``absolute non-blood transfusion'' (the position or idea that blood should not be transfused under any circumstances, respecting the will of the patient). I am choosing.
MEDIUS Group is developing a business centered on the sale of medical equipment. We (Medical + us) involved in medical care also want to play the role of an information source (Media) that delivers useful information for the medical field and people's healthy tomorrow.