ASOURCE®NAVI

公開日:2024.03.07
抗生物質(抗菌薬)は肺炎など細菌による感染症の治療に不可欠ですが、抗菌薬の効かない薬剤耐性菌が増加し、世界的な脅威となっています。薬剤耐性のメカニズムや原因、対策などについてまとめます。なお、薬剤耐性は、細菌だけでなく、ウイルスや寄生虫でも確認されていますが、今回は細菌に限定してまとめます。
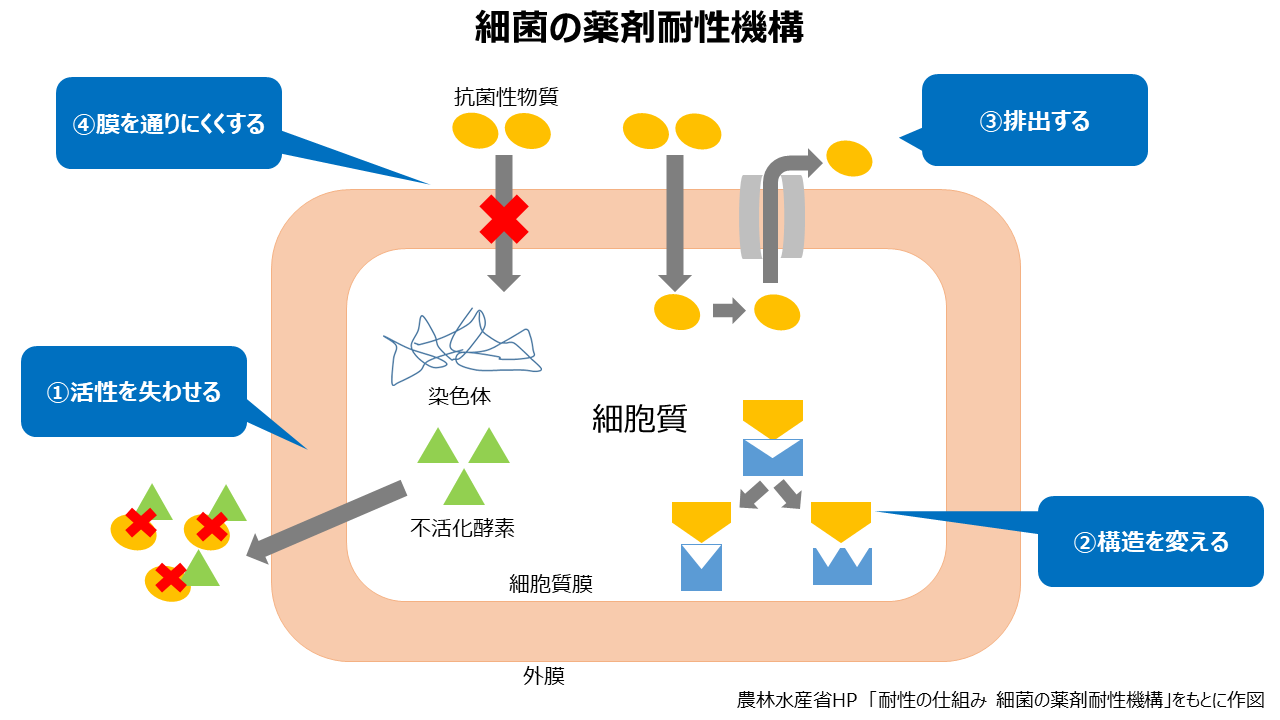
薬剤耐性とは、細菌が抗菌薬の効果に対して耐性を得て、抗菌薬が効きにくくなる、または効かなくなることを指します。耐性菌は遺伝的な変異により、抗菌薬の作用機序を回避するようになるため、死滅させることができなくなります。細菌が薬剤耐性を獲得する機構としては、
①抗菌性物質を分解する酵素を産生し、活性を失わせる
②細菌の構造を変えて、抗菌性物質の作用を阻害する
③抗菌性物質を細菌内から排出する
④膜を通りにくくし、抗菌性物質を細菌内に入れない
などが知られています。
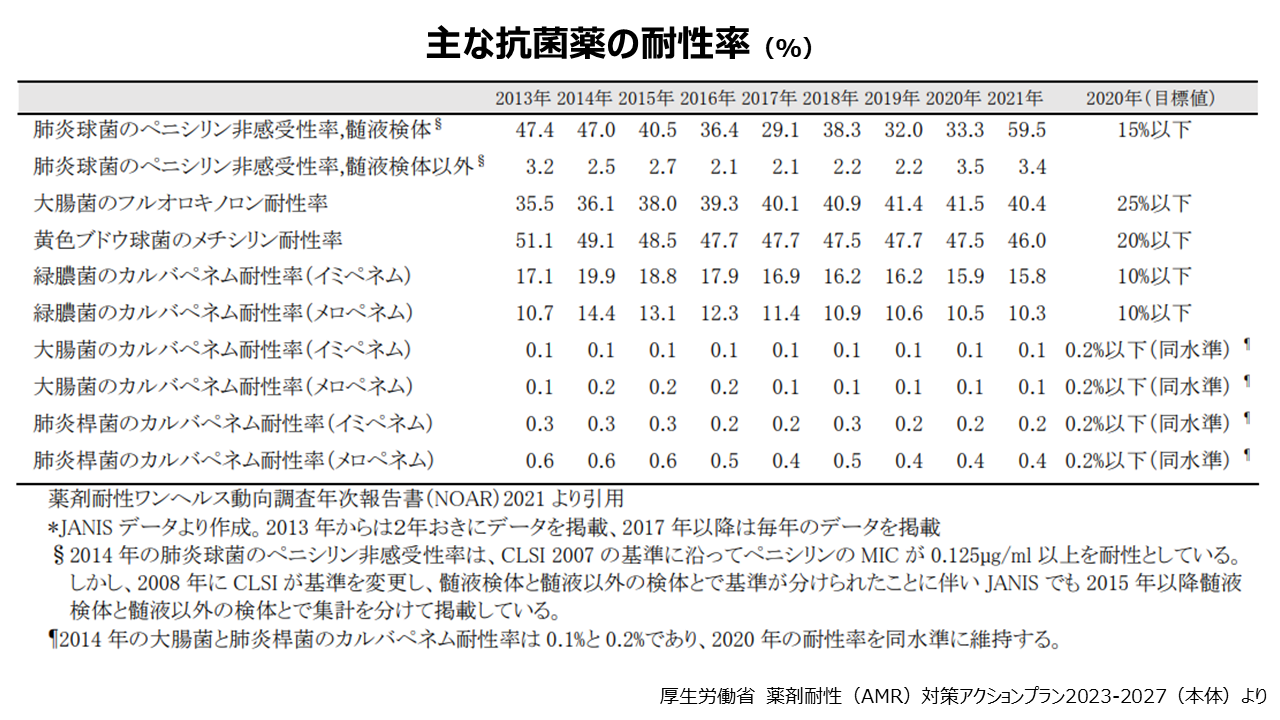
薬剤耐性菌による死亡者数は全世界で年間100万人を超えていると推計されていますが、2050年までに年1千万人に達するという予測を、2014年に英政府が発表しています。世界保健機関(WHO)は耐性菌を「健康に対する最大の脅威の一つ」と位置づけています。肺炎球菌、メチシリン耐性黄色ブドウ球菌(MRSA)、結核菌、フルオロキノロン耐性大腸菌(FQREC)など多くの菌種で重度の耐性化が報告されており、WHOの2012年の報告によると、世界的な肺炎球菌のペニシリン耐性率は30%程度です。
日本では、2021年の肺炎球菌のペニシリン耐性率は約60%で、MRSAの検出率も50%近いとの報告があり、主要な病原体の耐性化が進行しています。2019 年の国内調査において、薬剤耐性菌の中でも頻度が高いMRSA及びFQRECの菌血症による2017 年の年間死亡者数が 8,000 人以上と推定されるという研究報告がされています。さらに治療困難なケースが増えているとされ、深刻な健康上の脅威として取り上げられ、薬剤耐性対策は重要な課題となっています。
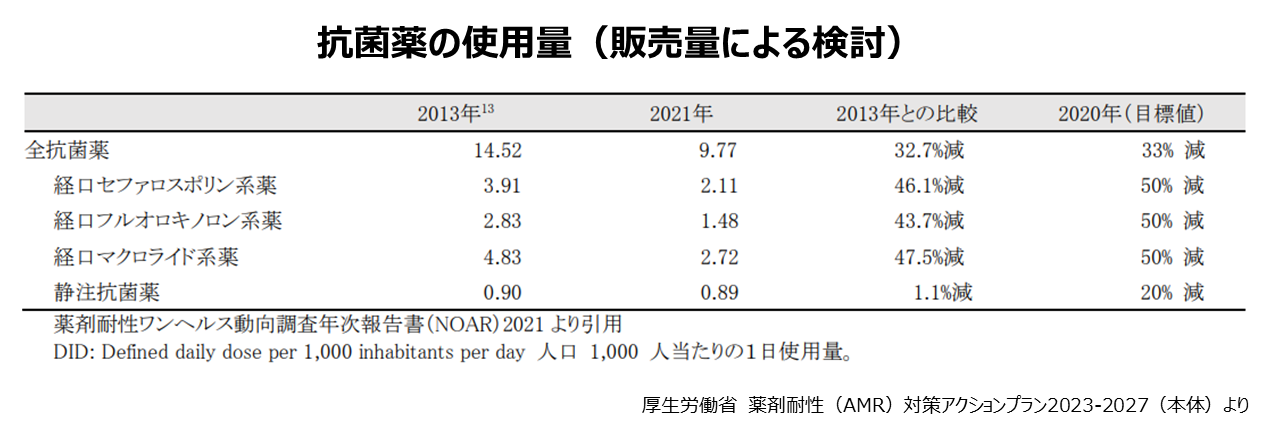
薬剤耐性の主な原因は、抗菌薬の不適切な使用です。患者が処方された抗菌薬を服用するのを途中でやめたり、飲んだり飲まなかったりの不適切な飲み方をすると、薬剤耐性菌が出現し、抗菌薬が効きにくくなってしまいます。 そのため、抗菌薬は指示された通りに服用し、最後まで飲み切ることが大切です。または医師が必要以上に抗菌薬を処方することで、菌が薬剤に対する耐性を獲得します。政府は2016年から、抗菌薬をむやみに使わないようにするなど、対策を進め、2021年には、2013年に比べて使用量は約33%減りました。 しかし、未だ外来診療での抗菌薬の不適切な処方が散見されるといわれます。抗菌薬は細菌による感染症の治療に使う薬なので、普通の風邪などウイルスによる感染症には、抗菌薬は効果がありませんが、患者から抗菌薬の処方を医者に依頼するケースもみられます。また、農業での抗生物質の使用や獣医学での使用も薬剤耐性の拡大に影響しています。
耐性菌が蔓延すると、薬で治療できない感染症で苦しむ人が増えるだけでなく、外科手術や臓器移植といった医療システムも機能しなくなる恐れがあります。耐性菌への対策には、国を越えた取り組みが欠かせません。WHOは世界行動計画を策定し、各国への政策支援を行っています。日本でも厚生労働省がアクションプランを作成し、
・抗菌薬使用の適正化
・抗菌薬の研究開発と教育
・国際協力の強化
等を柱とした対策に取り組んでいます。
メディアスグループは、医療機器の販売を中心とした事業を展開しています。医療に携わる私たち(Medical+us)は、医療現場や人々の健康的な明日へ役立つ情報をお届けする情報発信源(Media)の役割も果たしていきたいと考えています。